The head of the World Health Organisation (WHO) believes the ongoing mpox outbreaks in Africa might be stopped in the next six months, and said on Friday that the agency’s first shipment of vaccines should arrive in Congo within days.
To date, Africa has received just a tiny fraction of the vaccines needed to slow the spread of the virus, especially in Congo, which has the most cases – more than 18,000 suspected cases and 629 deaths.
“With the governments’ leadership and close co-operation between partners, we believe we can stop these outbreaks in the next six months,” WHO director-general Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus said at a press briefing.
He said that while mpox infections have been rising quickly in the last few weeks, there have been relatively few deaths. Tedros also noted there were 258 cases of the newest version of mpox, with patients identified in Burundi, Rwanda, Kenya, Uganda, Sweden and Thailand.

Earlier this month, WHO declared the ongoing mpox outbreaks in Africa a global emergency, hoping to spur a robust, global response to the disease on a continent where cases were spreading largely unnoticed for years, including in Nigeria.
In May, scientists detected a new version of the disease in Congo that they think could be spreading more easily.
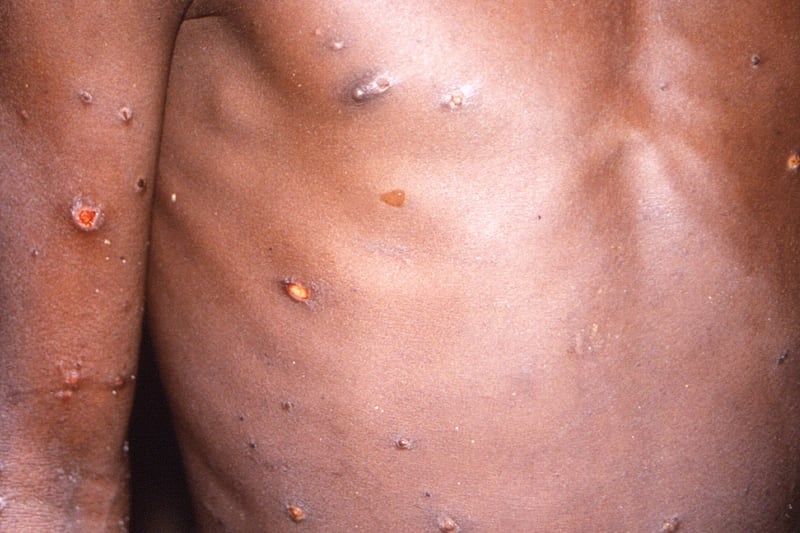
Mpox, also known as monkeypox, is related to smallpox but typically causes milder symptoms, including fever, headache and body aches.
In severe cases, people can develop painful sores and blisters on the face, chest, hands and genitals.
Mpox is typically spread via close skin-to-skin contact.
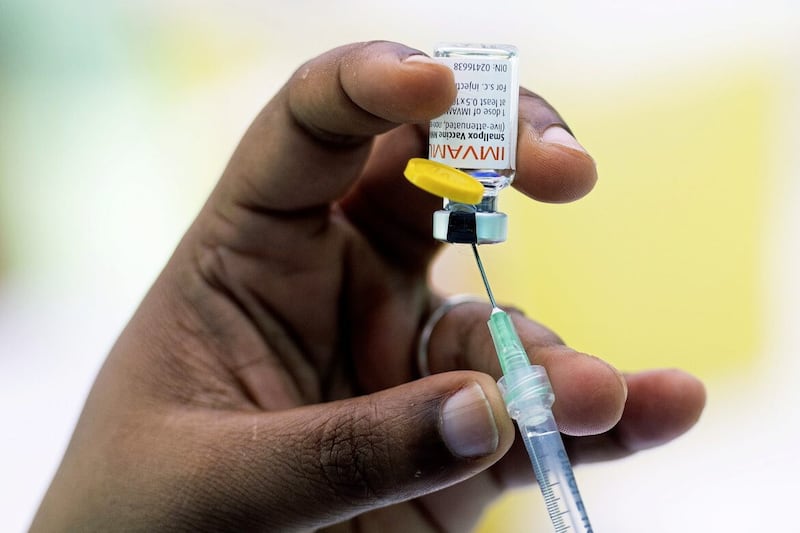
WHO estimated about 230,000 vaccines could be sent “imminently” to Congo and elsewhere.
The agency said it was also working on education campaigns to raise awareness of how people could avoid spreading mpox in countries with outbreaks.
Maria Van Kerkhove, who directs WHO’s epidemic and pandemic diseases department, said the agency was working to expedite vaccine access for affected countries – given the limited supply available.
Scientists have previously pointed out that without a better understanding of how mpox is spreading in Africa, it may be difficult to know how best to use the shots.
Earlier this week, the head of Africa’s Centres for Disease Control and Prevention said the continent was hoping to receive about 380,000 doses of mpox vaccines promised by donors, including the US and the European Union.
That’s less than 15% of the doses authorities have said are needed to end the mpox outbreaks in Congo.